Blockchain technology has transformed the way we handle digital transactions and data storage. It serves as a secure and decentralized platform that records and verifies information without intermediaries.
Imagine a digital ledger that’s shared among a network of computers, where each transaction is securely recorded, transparently visible, and impossible to alter. That’s the core idea behind blockchain—a revolutionary concept with the potential to reshape how we interact online. In this blog, we’re here to break down the basics of blockchain in simple terms. We will learn about how does blockchain work and the intricacies involved in blockchain technology! But first, let’s get to know what blockchain is all about!
Blockchain is a technique for storing data that makes it difficult or impossible for outside parties to alter, hack, or manipulate the system. A distributed ledger, or blockchain, is a network of computers that replicates and disperses transactions between itself.
Blockchain technology is a framework that uses many databases, referred to as the “chain,” connected by peer-to-peer nodes, to store public transactional records or blocks. This type of storage is commonly known as a “digital ledger.”
The digital signature of the owner authorizes each transaction in this ledger, ensuring its authenticity and preventing any manipulation. Because of this, the data in the digital ledger is extremely safe.
To put it another way, the digital ledger is essentially a network of several computers sharing a Google spreadsheet where transactional data are kept according to real purchases. The intriguing aspect is that while everyone may view the data, it cannot be altered.
You may have seen that a growing number of companies worldwide have been utilizing Blockchain technology in recent years. But how does the blockchain work specifically? Is this a little addition or a big change? Let’s start by dispelling some of the myths surrounding Blockchain technology, as these developments are still in their infancy and might become revolutionary in the future.
Blockchain combines three innovative technologies:
The two keys used in cryptography are the public key and the private key. These keys facilitate the effective completion of transactions between two parties. These two keys belong to each person, and they are used to create a safe digital identity reference. Perhaps the most significant feature of Blockchain technology is this encrypted identification. This identification, known as a “digital signature” in the context of cryptocurrencies, is used to authorize and manage transactions.
The peer-to-peer network and the digital signature are combined, and a lot of people who function as authorities use the digital signature to agree on transactions and other matters. A mathematical verification confirms their approval of a contract, leading to a successful safe transaction between the two network-connected parties.
There are different types of blockchain. They are as follows.
Private blockchains run on closed networks and are best suited for private corporations and organizations. Companies may utilize private blockchains to tailor their access and permission preferences, network characteristics, and other critical security features. A private blockchain network is managed by just one authority.
Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies evolved from public blockchains, which also helped popularize distributed ledger technology (DLT). Public blockchains also assist to avoid some obstacles and issues, such as security weaknesses and centralized control. DLT distributes data throughout a peer-to-peer network rather than storing it in a single location. A consensus technique is used to verify information validity; proof of stake (PoS) and proof of work (PoW) are two popular consensus approaches.
Permissioned blockchain networks, also known as hybrid blockchains, are private blockchains that provide unique access to approved persons. Organizations generally build up these sorts of blockchains to obtain the greatest of both worlds, as it allows for better organization when determining who may join the network and in which transactions.
Read Blog: Permissionless Blockchain: An Overview
Consortium blockchains, like permissioned blockchains, feature both public and private components, but they are managed by numerous organizations. Although these sorts of blockchains are initially more difficult to set up, once operational, they can provide superior security. Furthermore, consortium blockchains are ideal for collaboration across various enterprises.
Hybrid blockchains combine both public and private blockchains. In a hybrid blockchain, certain sections of the blockchain are public and transparent, but others are private and only available to authorized members. This makes hybrid blockchains excellent for applications that demand a mix of openness and secrecy. For example, in supply chain management, numerous parties can view some information but sensitive data is kept secret.
Sidechains are parallel blockchains that provide extra features and scalability. Sidechains allow developers to get creative with new features and apps without compromising the main blockchain’s integrity. Sidechains can also be utilized to manage transactions of the main blockchain, reducing congestion and enhancing scalability.
Building several blockchain layers on top of one another is referred to as “blockchain layers.” Every layer can have its own rules, functionality, and consensus mechanism that can communicate with other levels. Due to the capacity to handle transactions concurrently across many levels, this guarantees increased scalability. As an illustration, the Lightning Network is a second-layer solution that facilitates quicker and less expensive transactions by opening up payment channels between users and is built on top of the Bitcoin blockchain.
Read Our Blog: Layer-1 Vs. Layer-2: The Blockchain Scaling Solutions
Blockchain as a Service (BaaS) is a cloud-based service that allows users to develop, host, and deploy blockchain applications without the complexity of building and maintaining the underlying infrastructure typically associated with blockchain technology.
Similar to other “as a Service” models like Software as a Service (SaaS) or Platform as a Service (PaaS), BaaS provides users with access to blockchain capabilities on a pay-as-you-go or subscription basis. This means that users can leverage the benefits of blockchain technology, such as decentralization, transparency, and immutability, without needing to invest in hardware, software, or specialized expertise.
Here’s how it works:
1. Cloud-Based Infrastructure: Blockchain as a Service (BaaS) providers offer blockchain infrastructure hosted on their cloud platforms. This infrastructure typically includes all the necessary components for deploying, managing, and scaling blockchain networks.
2. Pre-Built Solutions: BaaS platforms often provide pre-built blockchain solutions and templates tailored for specific use cases, such as supply chain management, identity verification, or financial transactions. These solutions come with predefined smart contracts, consensus mechanisms, and other necessary features.
3. Development Tools: BaaS platforms offer a range of development tools, APIs, and SDKs that enable developers to easily build, test, and deploy blockchain applications. These tools abstract away much of the complexity associated with blockchain development.
4. Scalability and Flexibility: BaaS platforms typically offer scalability features, allowing customers to easily scale their blockchain networks based on demand. They also provide flexibility in terms of choosing the underlying blockchain protocol, consensus mechanism, and other configuration options.
5. Managed Services: BaaS providers handle various operational aspects of the blockchain infrastructure, such as security, maintenance, and upgrades. This allows customers to focus on developing and deploying their applications without worrying about the underlying infrastructure.
Blockchain technology has found applications across various industries, revolutionizing processes and enhancing security and transparency. Let’s explore how blockchain is utilized in different sectors:
In the financial industry, blockchain is widely used for secure and transparent transactions. It has facilitated faster cross-border payments, reduced transaction costs, and minimized the need for intermediaries. Smart contracts powered by blockchain technology automate processes such as loan approvals and trade settlements, streamlining operations and reducing the risk of fraud.
Blockchain is transforming the healthcare sector by improving data management and patient care. Electronic health records stored on blockchain platforms ensure data integrity and confidentiality, enabling secure sharing of information among healthcare providers. Additionally, blockchain in healthcare facilitates drug traceability, ensuring the authenticity of pharmaceutical products and combating counterfeit drugs in the market.
Blockchain technology is reshaping supply chain management by enhancing transparency and traceability. By recording every step of a product’s journey on a of transparency builds trust among stakeholders and improves overall supply chain efficiency.
In the real estate industry, blockchain is revolutionizing property transactions and ownership records. Smart contracts on blockchain platforms enable secure and transparent real estate transactions, eliminating the need for intermediaries such as brokers and lawyers. Blockchain-based property registries ensure accurate and tamper-proof records of ownership, reducing the risk of fraud and disputes in real estate transactions.
Read Blog: Revolutionizing Real Estate With Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology is being leveraged in the energy sector to enable peer-to-peer energy trading and enhance grid management. Through blockchain-based platforms, energy producers can sell excess energy directly to consumers, creating a decentralized energy market. Smart meters integrated with blockchain technology enable real-time monitoring of energy consumption and transactions, promoting energy efficiency and sustainability.
These examples showcase the diverse applications of blockchain technology across industries, highlighting its potential to revolutionize processes, enhance security, and drive innovation in various sectors.
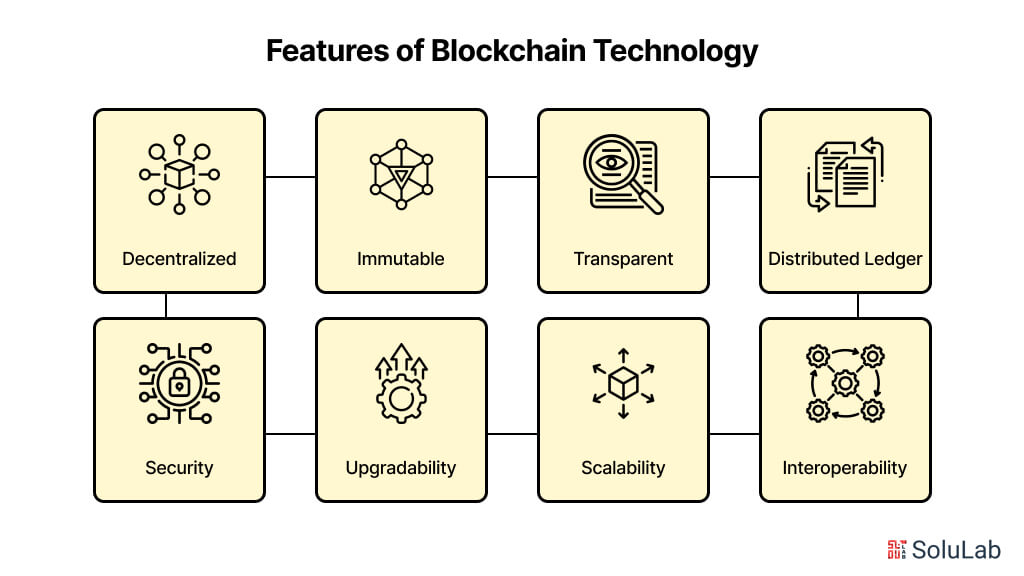
Here are the key features of blockchain technology:
1. Decentralized: Blockchain is a decentralized system, meaning that there is no single central authority controlling the network. Instead, it is maintained by a network of nodes (computers) that work together to validate transactions.
2. Immutable: Once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted. This is because each block is linked to the previous block through a unique code, making it impossible to change or manipulate the data.
3. Transparent: All transactions on the blockchain are transparent, meaning that anyone can view the entire history of transactions on the network.
4. Distributed Ledger: Blockchain is a distributed ledger technology, meaning that multiple nodes on the network maintain a copy of the entire blockchain, ensuring that all parties have access to the same information.
5. Security: Blockchain technology uses advanced cryptography and encryption techniques to ensure that all transactions are secure and tamper-proof.
6. Upgradability: Many blockchain networks are designed to be upgradable, allowing for changes to be made to the protocol or underlying code without disrupting the network.
7. Scalability: While blockchain technology has made significant progress in terms of scalability, some networks still face limitations in terms of transaction speed and capacity.
8. Interoperability: Blockchain technology is being developed to enable interoperability between different networks, allowing for seamless communication and data exchange between different ecosystems.
Since its first release in 2009, Bitcoin has grown to become the most well-known and prosperous virtual currency to date. Due to its decentralized nature—that is, the lack of a central bank or body overseeing its supply—Bitcoin has become extremely popular. This implies that utilizing Bitcoin entails no transaction costs and anonymous transactions.
Blockchain is a database of past transactions between two parties. As new transactions occur, blocks of data containing details about them are added to the chain in chronological order. The amount of blocks generated following a record makes it harder to modify over time, therefore the Blockchain is always expanding as new blocks are added to it.
Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize various industries and sectors beyond its original use case in cryptocurrency. The decentralized and secure nature of blockchain makes it an attractive solution for a wide range of applications, including:
Blockchain technology has numerous benefits that make it an attractive solution for various industries and sectors. Some of the key benefits of blockchain technology include:
1. Increased Transparency: Blockchain technology provides a transparent and tamper-proof record of transactions, making it easier to track and verify the authenticity of data.
2. Improved Security: Blockchain technology uses advanced cryptography and encryption techniques to ensure that data is secure and tamper-proof, making it difficult for hackers to access or manipulate data.
3. Reduced Costs: Blockchain technology can reduce costs by automating processes, eliminating intermediaries, and increasing efficiency.
4. Enhanced Efficiency: Blockchain technology can automate processes, reduce the need for manual intervention, and increase speed and accuracy, making it an attractive solution for industries that require fast and efficient processing.
5. Increased Trust: Blockchain technology can increase trust between parties by providing a secure and transparent record of transactions, making it easier to establish trust in digital transactions.
6. Decentralized Control: Blockchain technology allows for decentralized control, giving individuals and organizations more control over their data and transactions.
7. Improved Data Accuracy: Blockchain technology can improve data accuracy by providing a single source of truth, reducing the risk of errors and inconsistencies.
8. Reduced Risk of Fraud: Blockchain technology can reduce the risk of fraud by providing a secure and transparent record of transactions, making it difficult for fraudsters to manipulate data.
9. Increased Accessibility: Blockchain technology can increase accessibility by providing a secure and transparent way for individuals and organizations to access and share data.
10. Scalability: Blockchain technology can scale to meet the needs of growing industries and sectors, providing a secure and transparent way to manage large amounts of data.
11. Improved Compliance: Blockchain technology can improve compliance by providing a secure and transparent record of transactions, making it easier to meet regulatory requirements.
12. Reduced Counterfeiting: Blockchain technology can reduce counterfeiting by providing a secure and transparent way to track the origin and movement of goods.
13. Improved Supply Chain Management: Blockchain technology can improve supply chain management by providing a secure and transparent way to track the movement of goods.
14. Enhanced Customer Experience: Blockchain technology can enhance customer experience by providing a secure and transparent way to manage customer data and transactions.
15. Increased Value: Blockchain technology can increase value by providing a secure and transparent way to manage digital assets, such as cryptocurrencies.
Overall, blockchain technology has the potential to bring significant benefits to various industries and sectors, from improved security and transparency to increased efficiency and accessibility. As the technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more innovative applications of blockchain emerge.
There are a lot of blockchain platforms out there. The Ethereum blockchain, Hyperledger Fabric, and OpenChain are the three most well-known.
1. Ethereum: Ethereum stands as one of the most widely utilized and respected blockchain platforms in the industry. It is celebrated for its open-source nature and adaptability, making it a preferred choice for various enterprise applications. One of Ethereum’s groundbreaking contributions to the blockchain space is the introduction of smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps). These innovations have significantly expanded the potential use cases of blockchain technology beyond simple transactions. Ethereum boasts a robust and expansive developer community, fostering continuous innovation and development within its ecosystem. Its native cryptocurrency, Ether, serves as the fuel for executing operations on the platform.
2. Hyperledger Fabric: Hyperledger Fabric caters to specific industry needs, particularly in the finance and manufacturing sectors. It is an open-source blockchain platform designed primarily for permissioned networks. However, it can also support decentralized hosting and storage of applications leveraging smart contracts. Hyperledger Fabric offers a modular framework that empowers organizations to build private blockchains customized to their unique business requirements. This flexibility, combined with its support for smart contracts, enables diverse applications across various industries.
3. OpenChain: OpenChain addresses the requirements of organizations looking to efficiently manage and safeguard digital assets. As an open-source blockchain platform, it allows administrators to establish the rules governing the ledger. Users can then engage in value exchange on the ledger while adhering to these predefined rules. OpenChain’s focus on providing a customizable and scalable solution makes it suitable for a wide range of use cases, from supply chain management to digital asset issuance and tracking.
In conclusion, the blockchain represents a revolutionary technology with the potential to transform numerous industries by providing secure, transparent, and decentralized solutions for various applications. Its underlying principles of immutability, decentralization, and cryptographic security make it a robust and reliable platform for storing and exchanging digital assets and information. From financial transactions and supply chain management to identity verification and decentralized applications, the blockchain offers endless possibilities for innovation and disruption.
As businesses and organizations continue to explore the benefits of blockchain technology, partnering with an experienced blockchain development company becomes crucial. SoluLab stands out as a leading provider of blockchain solutions, offering expertise in developing custom blockchain applications tailored to specific business requirements. With a team of skilled developers and blockchain specialists, SoluLab empowers businesses to harness the full potential of blockchain technology. Whether it’s creating decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms, supply chain tracking systems, or secure digital identity solutions, SoluLab delivers reliable, scalable, and innovative blockchain solutions. Contact us today to embark on your blockchain journey and unlock new opportunities for growth and innovation.
Blockchain technology is a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions across a network of computers in a secure and transparent manner. Each block in the chain contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, creating a chronological and immutable record of transactions.
Blockchain ensures security and trust through its decentralized nature and cryptographic mechanisms. Transactions on the blockchain are verified and recorded by multiple participants in the network, making it extremely difficult for any single entity to tamper with the data. Additionally, cryptographic techniques like hashing and digital signatures provide further security by encrypting and authenticating transactions.
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. These contracts automatically execute and enforce themselves when predetermined conditions are met, eliminating the need for intermediaries. Smart contracts run on blockchain platforms like Ethereum, leveraging the platform’s decentralized infrastructure to ensure transparency and security.
While blockchain technology gained prominence with the rise of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, its utility extends far beyond digital currencies. Blockchain can be applied to various industries and use cases, including supply chain management, healthcare, finance, voting systems, and identity verification. Its decentralized and immutable nature makes it suitable for any scenario requiring secure and transparent record-keeping.
Businesses can leverage blockchain technology in numerous ways to streamline operations, enhance security, and drive innovation. Some common applications include supply chain tracking to improve transparency and traceability, digital identity management to securely verify user identities, and decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms for efficient and transparent financial transactions. By incorporating blockchain into their operations, businesses can gain a competitive edge and unlock new opportunities for growth and efficiency.